Optical Filters: Filters are optical devices used to select the desired band of radiation. Filters can selectively transmit a portion of the spectrum while rejecting the rest. Optical filters are commonly used in microscopy, spectroscopy, chemical analysis and machine vision.
Transmittance (T): Assuming that the initial value of the light is 100%, through the filter will be lost, through the post-test only the initial value of 80%, then the optical transmittance of the filter is said to be only 80%.
Center Wavelength (CWL): The center wavelength used to define the bandpass filter describes the midpoint of the spectral bandwidth above which the filter transmits. Specifically refers to the wavelength of the bandpass filter used in the actual application, such as the main peak value of the light source is 800nm LED lamps, the demand for the center wavelength is 800nm.
Full Width at Half Maxima (FWHM): Full width at half maxima, or FWHM for short, is used to describe the spectral bandwidth that a bandpass filter will transmit. It means that the upper and lower limits of this bandwidth are defined at the wavelength at which the filter reaches its maximum transmittance of 50%. For example, if the maximum transmittance of the filter is 90%, then the wavelength at which the filter reaches a transmittance of 45% would define the upper and lower limits of the FWHM. 10nm or less is considered narrowband and is commonly used in laser cleanup and chemical detection. 25-50nm FWHM is commonly used in machine vision applications; FHWM over 50nm is considered broadband and is commonly used in fluorescence microscopy applications. FHWMs above 50nm are considered broadband and are commonly used in fluorescence microscopy applications.
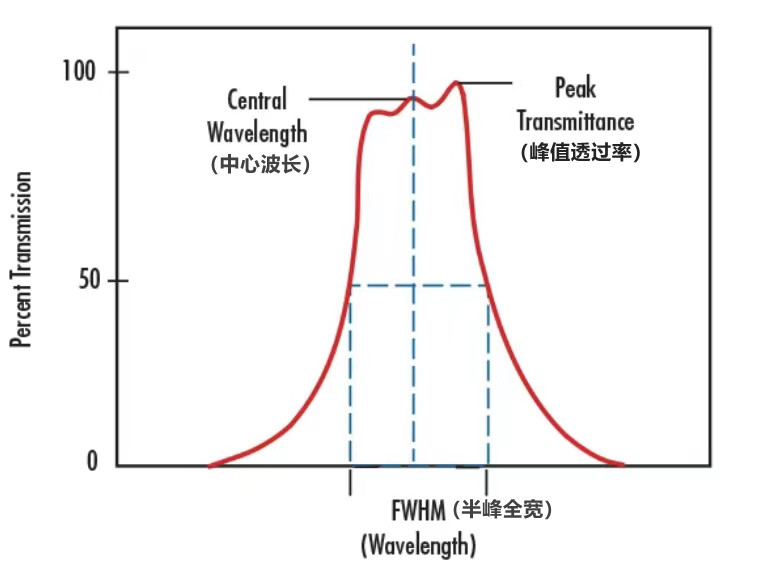
Peak transmittance, center wavelength, and half-peak full width illustration charts
