Introduction to Enzyme Labeling Instruments
ELISA, i.e. enzyme-linked immunoassay tester, is a special instrument for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). In fact, it is a special photoelectric colorimeter or spectrophotometer in disguise, and its basic working principle and main structure and photoelectric colorimeter are basically the same. Can be simply divided into semi-automatic and fully automatic 2 categories, but its working principle is basically the same, the core is a colorimeter, that is, the colorimetric method to analyze the content of antigen or antibody.
What is an enzyme assay
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method, referred to as ELISA, is one of the labeling techniques, which is a sensitive, specific, rapid and automated modern technique developed from fluorescent antibody and isotope immunization techniques.
The basic principle of the enzyme assay is to combine antigen or antibody with enzyme using a collagen to form an enzyme-labeled antigen or antibody, which can react specifically with the corresponding antigen or antibody on the solid-phase carrier or in the tissue, and bind firmly to form an immune complex that remains active. When the corresponding substrate is added, the substrate is catalyzed by the enzyme and shows the corresponding reaction color. The color is proportional to the amount of the corresponding antigen or antibody.
Since this technique is based on the antigen-antibody reaction and the efficient catalytic action of enzymes, it is highly sensitive and specific, making it an extremely viable immunological test technique.
Principle of Enzyme Labeling Instrument
Enzyme labeling instrument is the application of the principle of enzyme labeling instrument, enzyme labeling instrument is similar to a variable phase photoelectric colorimeter or spectrophotometer, its basic working principle and the main structure and photoelectric colorimeter is basically the same.
The light emitted by the light source lamp through the filter or monochromator into a beam of monochromatic light, into the plastic microporous pole to be measured specimen. Part of the monochromatic light is absorbed by the specimen, the other part is irradiated through the specimen to the photoelectric detector, the photoelectric detector will be different specimens to be tested and the intensity of different light signals into the corresponding electrical signals, electrical signals by the preamplifier, logarithmic amplification, analog-to-digital conversion and other signal processing sent to a microprocessor for data processing and calculations, and then by the display and the printer to show the results.
The microprocessor also moves the microplate by controlling the movement of the mechanical drive mechanism in the X- and Y-directions through a control circuit, thus realizing the automated injection detection process. Other enzyme markers use manual movement of the microplate for detection, thus eliminating the mechanical drive mechanism and control circuitry in the X and Y directions, resulting in a smaller and simpler instrument.
Microtiter plate is a transparent plastic plate specially designed for placing the samples to be tested by prior treatment, there are many rows of small holes of uniform size on the plate, the holes are embedded with the corresponding antigens or antibodies, and each hole on the microtiter plate can hold a few milliliters of solution. Its common specifications are 40-well plate, 55-well plate, 96-well plate and so on, different instruments use different specifications of the plate, which can be detected hole by hole or row by row.
An ELISA assay is the detection of the absorbance value of a measured substance at a specific wavelength. With the development of assays, single benchtop enzyme markers with multiple detection modes are called multifunctional enzyme markers, which can detect absorbance (Abs), fluorescence intensity (FI), time-resolved fluorescence (TRF), fluorescence polarization (FP), and chemiluminescence (Lum).
Enzyme markers can be categorized into grating enzyme markers and filter enzyme markers in terms of principle. Grating-type enzyme markers can intercept any wavelength within the wavelength range of the light source, while filter-type enzyme markers can only intercept specific wavelengths for detection according to the optional filters.
Enzyme Labeling Instrument Structure
The monochromatic light used in the enzyme marker can be obtained either by coherent filters or by the same monochromator of the spectrophotometer. In the use of filters as a filter device with the ordinary colorimeter, the filter can be placed in front of the microplate, can also be placed behind the microplate, the effect is the same. The light emitted by the light source lamp through the concentrating mirror, the light column after reaching the reflector, the reflector for 90 ° reflection vertically through the colorimetric solution, and then sent to the photoelectric tube through the filter.
Enzyme labeling instruments can be divided into 2 types: single-channel and multi-channel, and single-channel can be divided into 2 types: automatic and manual. The automatic type has a mechanical drive mechanism in X and Y direction, which can send the small wells of the microplate L one by one under the beam of light for testing, while the manual type relies on manual movement of the microplate to carry out measurements.
On the basis of single-channel enzyme labeling instrument has developed multi-channel enzyme labeling instrument, such enzyme labeling instrument is generally automated type. It is equipped with multiple light beams and multiple photodetectors, such as 12 channels of the instrument is equipped with 12 light beams or 12 light, 12 detectors and 12 amplifiers, in the X-direction of the mechanical drive device under the action of the samples 12 for a row to be detected. Multi-channel enzyme labeling instrument detection speed, but its structure is more complex price is also higher.
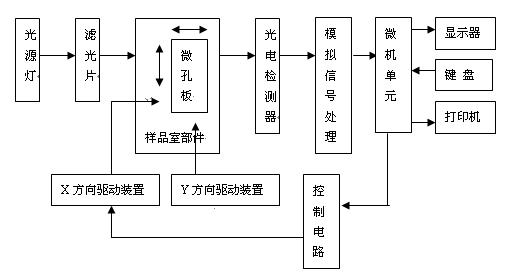
Enzyme Labeling Instrument Schematic Diagram
